Integrated Mobile Manipulation &
Kinematic Control for Kuka YouBot
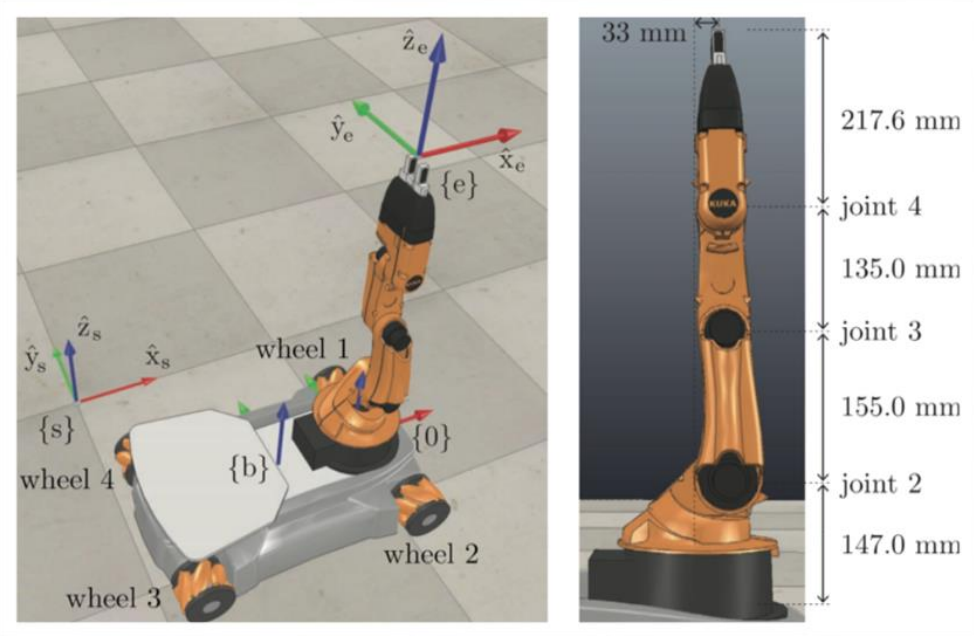
Architected a unified 8-DOF control system for the Kuka YouBot, implementing custom kinematic solvers to synchronize holonomic base navigation with precise robotic arm positioning.
To achieve fluid "reach-and-grasp" capabilities in a simulated environment, I developed a comprehensive control framework that treated the Kuka YouBot’s omnidirectional platform and 5-DOF arm as a single, cohesive unit. By deriving and implementing custom Forward and Inverse Kinematics (FK/IK) from first principles, I enabled the robot to execute complex object-moving tasks with mathematical precision while respecting the physical constraints of real-world hardware.
Technical Challenges & Solutions
The Redundancy Problem: With 8 total degrees of freedom (3 from the base, 5 from the arm), there are infinite ways to reach a coordinate. I engineered a solver that optimized for the "sweet spot" of the arm's reach, using the mobile base to position the robot so the arm always operated within its most dexterous workspace.
Singularity Avoidance: Custom IK solvers often fail at extreme joint angles. I implemented numerical methods in Python to handle mathematical singularities, ensuring smooth, continuous motion during high-precision pick-and-place maneuvers.
Sim-to-Real Fidelity: To ensure the simulation was a true Digital Twin, I integrated the exact mass, torque limits, and velocity constraints of the physical YouBot. This allowed the Python-based controller to govern the CoppeliaSim model as if it were the physical machine.
Technical Stack
Control Logic: Python (NumPy for high-speed matrix calculations)
Simulation Environment: CoppeliaSim (formerly V-REP)
Communication: ZeroMQ / Remote API for real-time synchronization
Mathematical Modeling: Denavit-Hartenberg (D-H) parameters and Holonomic Drive equations
Engineering Highlights
Unified Motion Planning: Developed a "Whole-Body Control" approach where the base and arm move simultaneously, significantly reducing the time required to complete manipulation tasks.
Custom Geometric Solvers: Built the FK/IK engine from scratch rather than using black-box libraries, allowing for granular control over individual joint priorities and obstacle avoidance.
Holonomic Precision: Leveraged the 4-wheel omnidirectional drive to allow for translation and rotation in any direction, providing a level of maneuverability that standard differential-drive robots cannot achieve.